Types of trading: comprehensive guide
What types of trading are there? How do they differ? Which type is good for a novice trader and which one suits an experienced trader?
Trading as a way of earning profits has been gladly adopted by people. Someone’s gains are enough for a few visits to a grocery store, whereas someone can afford to buy a car, property, etc. with this extra income.
The financial result of this business mainly depends on how well people explored types of trading and whether they picked the right trading style. Read the article to grasp the ins and outs of the subject.
Idea of trading
The classic idea of trading means trading securities, currencies, and other assets. The goal of this activity is to gain profits.
A profit is generated because assets are bought at a lower price and later sold at a higher price. It is the essence of speculative operations. People have been occupied with speculating for a few centuries. First speculators sprang up almost at the same time when money came into being.
Society has expressed different attitudes toward speculators throughout history.
At some stages in history, public opinion used to consider speculative activity not only shady but even unlawful. Trading was recognized as a fully legal way of earning worldwide only when authorities greenlighted official trading or exchange floors.
Nowadays, trading represents a complicated system consisting of numerous trading platforms, participants, and regulators. Each of them has its own role.
As a rule, retail traders carry out their activity through brokers and third parties which act as mediators between exchanges and market participants.
Investors are another category of market participants. Their striking difference from traders is that investors aim for longer-term capital manipulation and diversification of an investment portfolio.
Unlike them, traders strive to gain fast profits, for example, during one trading day or an hour. By contrast, investors pursue long-term strategies which could last for several years.
Besides, investors distribute their funds to make up individual portfolios that could consist of dozens of various assets. Such market participants commonly have remarkable skills in fundamental analysis which is an integral part of long-term investing.
Categories of market participants
A buy/sell transaction is always executed by two sides. One side is buyers who are also termed bulls.
Their activity boosts demand for assets. As a result, market quotes of securities, currencies, and other instruments go higher. Indeed, market quotes are directly linked to a demand/supply ratio: if demand increases, a market quote goes up; if supply increases, a market quote goes down.
Sellers are termed bears in the trading community. They actively sell shares, currencies, and other assets they hold, thus pushing market quotes down.
Next to some large exchange floors, for example, in the US and Germany, there are monuments to these basic categories of market participants, bulls and bears.
Interestingly, any trader may change roles in the cause of speculative activity. First, he may act as a bull, buying a particular asset. Later, he acts as a bear, willing to get rid of this asset. In the first case, the trader bets on the price increase. In the second case, he expects the price to fall.

How does it work on exchange floor?
It goes without saying that the price of any asset develops in waves: it rises and falls in regular patterns during a particular period within a trend channel. This channel is capped by two lines: support and resistance as shown in the chart.
When the price approaches support, i.e. the lowest value, the bulls understand that it is the right time to buy an asset because it is cheap. They enter the market and open long (buy) positions. In turn, the price rallied because of growing demand.
When the chart is approaching resistance, the bears take the lead in the market as they aim to sell the asset at an ultimate high price. Growing supply enables the price to kick out of the resistance line and again go down.
The price makes the same moves until the balance of buyers and sellers breaks the current trend channel. Once this happens, the price creates new support and resistance levels over the cause of time.
To sum up, the bedrock of trading is a nonstop rivalry between bulls and bears. Each of the parties striving to earn sets the tone for a price dynamic.
Curiously, there are other categories of market participants who are given animal nicknames according to their behavioral patterns.
- Hares are traders who enter the market frequently but avoid making large bets.
- Pigs are greedy traders who want to receive the highest profit in the shortest possible time.
- Hamsters are those who begin their trading careers and make a lot of wrong decisions.
- Sheep are hesitant and unable to make prompt trading decisions.
- Wolves are professional traders with vast experience.
Types of trading
To ensure that trading fulfils its main goal of making profits, speculative activity should meet particular criteria. Importantly, the selected trading method should correspond to the market participant’s psychological features, personal traits, trading experience, and skills.
For example, scalping which implies managing plenty of positions in a short time hardly suits slow-thinking people, especially if they are new to the market.
Moreover, every trader sets various deadlines for achieving a particular financial result. In turn, such deadlines depend on the speed of executing transactions.
Trading can be differentiated according to the speed of managing trading positions.
- High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic trading to transact a large number of orders in fractions of a second.
- Scalping supposes that it takes seconds or minutes to execute a trade. Scalping and high-frequency trading are assigned to the same type of trading in some classifications.
- Day trading means that positions are opened and closed during one trading day. A trader does not extend open positions until the next day.
- Swing trading exploits short- to medium-term price movements. A trade may be kept for a term exceeding a trading day and may be closed in a few months. In some sources, this type is also defined as medium-term trading, though different definitions are suggested in other sources.
- In the case of long-term trading, an asset purchased may be stored for a few years. Investors should exercise a market vision to predict ultimate gains over a long course of time.
This type is the most efficient when investing in securities. Apart from returns from changes in stock quotes, holders of securities have a perk: they could be credited dividends.
Another classification of trading types suggests the following groups:
- Algorithmic trading implies the application of trading robots and expert advisors. These are special algorithms to forecast the direction of market quotes.
- Manual trading means that a trader is responsible for market analysis and forecasts.
In the table, find out the arguments for using algorithmic systems in trading. The results were obtained on the grounds of polls among market participants.

Specifics of HFT
We have already given you the idea of high-frequency trading (HFT) which is assigned to the category of algorithmic trading. Let’s expand in this type of trading.
High-frequency trading is a method of trading which requires milliseconds to open and close. Obviously, such a speed is beyond human nature. Therefore, the whole work is delegated to trading robots tailor-made for this task.
They explore the market on their own, carry out technical analysis, and then open and close positions, choosing the best moments for this. All these actions are executed at incredible speed. In other words, such programs perform the function of a trader. But they do it much faster than humans.
Features of HFT
- All trades are managed automatically without any involvement of a human trader.
- Accuracy and efficiency. The principle of trading robots is based on special algorithms which scan market quotes and make forecasts. Practical results have revealed the high accuracy of such forecasts which could be more than 90%.
- High-tech value. All trading robots are driven by special software developed by IT specialists.
High speed. Positions are opened and closed in fractions of a second or less than in a minute. No wonder, the number of orders managed by HFT is way bigger than humans can manage manually.
At first glance, it may seem that high-frequency trading is a sure-fire way of gaining profits which suits any trader. However, it is not true. A lot of retail traders cannot afford this trading method for obvious reasons.
- Too expensive. Trading robots are something that only large corporations and hedge funds can afford. So, they are too costly for the purse of most retail traders.
Creating one’s own trading algorithm is not always a solution because it is also a pricey method which requires IT and trading expertise. Besides, trading robots have to be maintained and upgraded because even cutting-edge software gets obsolete.
2. Powerful hardware is a must-have. If an individual trader designs one’s own robot for high-frequency trading, a powerful server is needed to set it in motion. Otherwise, the algorithms of competitors will run faster.
Nevertheless, the method of high-frequency trading has been gaining recognition among traders. The statistics show that HFT is the most popular way of trading securities. The second-popular method is futures contracts.
Specialists reckon that scalping could be the alternative to HFT for retail traders in terms of its simplicity.
Low-frequency trading
Low-frequency trading does not match all market participants. Speaking of scalping, fast execution of trades is also beyond the ability of many traders. Those traders who prefer a quieter and slower method may apply low-frequency trading (LFT).
It is common knowledge that in the case of LFT, a position can be kept open for more than one trading session of a day. You are certainly aware that a trend matters a lot to trading. Overall trading gains depend on whether a trader coped well to detect a particular trend.
LFT fans point out that the daily chart is more helpful and reliable in identifying a trend than shorter timeframes.
For example, a speculator may watch a bullish trend on a 1-minute chart whereas this upward move could happen to be an ordinary retracement on the daily chart. For this reason, traders choose in favor of low-frequency trading.
LFT advantages
- It saves time. A trader spends less time in front of a monitor or with a gadget to follow the trading routine.
- It ensures a more beneficial hypothetical risk/return ratio.
- It releases a trader from too much load and stress.
To prove the feasibility of low-frequency trading compared to other types of trading, let’s consider EUR/USD. The screenshot displays the daily chart where we can see a bullish breakout after the Pennant pattern has been formed. A profit could have been estimated at 500 pips in this case.
However, it could be complicated or even impossible to recognize this pattern on the 30-minute chart, i.e. in a shorter timeframe. It means that gaining a profit is an open question.
Importantly, we did not resort to trading robots in this example. In the case of HFT, they analyze the market themselves.

About quants
Most traders, especially beginners, adjust their trading decisions to technical analysis. Oftentimes, it is complemented by fundamental analysis.
Some professionals prefer quantitative trading above all other types. The cornerstone of this trading method is a plethora of quantitative data such as market quotes, trading volume, etc.
All available information is analyzed by special algorithms tailor-made for processing data through maths and statistics. As a result, a ready-made automated method is generated which enables a trader to yield gains.
Quants are specialists who develop this trading method.
The whole process of creating any quantitative method goes through the following stages:
- The analysis includes developing a strategy after scrutiny of data, for example, a price dynamic of a particular asset.
- Backtesting is the stage when developers can assess how the strategy is efficient under real market conditions.
- Order execution is the stage when the accomplished strategy is applied to trading conditions and a trading platform of a particular broker.
- The strategy is streamlined according to risk management.
To grasp the point of quantitative trading, let’s figure out an example of changes in the gold price for 15 years.
The chart represents the 12 months of the year. Each of the months is accompanied by a percent of the bullish trend cases in the last 15 years. All in all, January is the month when gold has traded with a bullish dynamic in most years.

This is a simple example of quantitative analysis. For a more detailed insight, analysts scrutinize not only seasonal dynamics.
Speaking of gold, analysts can apply the statistics on mining rates of the metal, its correlation with market quotes of currencies, etc. Quants may analyze a variety of patterns, depending on the degree of in-depth research.
As a result, they come up with a comprehensive analysis that will help to apply the whole batch of information for an accurate forecast of the gold dynamic in the future. Trading according to this algorithm is defined as quantitative.
Benefits from spoofing
Spoofing is a type of high-frequency trading. To explain the essence of this method, it is better to trace it back to its origin.
Nearly 10 years ago, one American market player sent to its brokerage firm more than 20,000 orders to buy oil futures contracts. However, he did not wait for their execution but canceled all of them. Everything happened in less than a second.
Such price manipulation aimed to create the illusion of growing oil demand which pushed oil prices sharply up. After this trick, the cunning trader who held some futures contracts sold them at a more beneficial price. The process described is called spoofing.
All countries take a different stance on such market manipulations, but in most countries, spoofing is banned at the legislative level.
Traders who practice this method are able to reap fat profits. In most cases, this activity is delegated to trading robots. Nevertheless, it poses a threat to retail traders. The thing is that other market participants are not able to sense spoofing and, as a result, respond to fake signals which, in turn, entail losses.
To avoid such incidents, traders should be aware that sometimes, market quotes move contrary to a forecast. One of the options to resist any tricks of a trader practising spoofing is to use charts with at least a 15-minute timeframe as an extra tool.
In this case, high-frequency correctional moves and market noise will be filtered out and you will not be confused by such dishonest ploys.
Front-running
Our review would be incomplete without telling you about another unethical and illegal practice like front-running. This method is used by some scalpers. The essence of front-running is exploiting insider information that has not yet been made public.
In practice, it works as follows. A trader sends a buy/sell order of modest size to a broker shortly before other market participants place larger orders. That trader is aware of insider information.
Here is another example. A large crypto trader plans to execute a hefty transaction with bitcoin which in theory is bound to drive up the asset’s price immediately. However, before he executes his transaction, another trader enters the market (commonly, he is of a smaller scale). The second one buys bitcoin at the current lower price. Later on, when the asset grows in value, he will sell the token at a profit.

Oftentimes, front-running is exploited not only by traders but also brokers. This form of front-running is illegal and unethical. The broker has made a profit based on information that was not public knowledge.
In world practice, there were even cases when the disclosed facts of front-running by brokers were prosecuted and punished with large fines.
This type of trading is widely applied to various assets such as securities, cryptocurrencies, DeFi, and even NFT.
Whereas front-running is based on insider information and thus considered illegal when trading stocks, it is a common practice for trading crypto. In this case, all data is freely available as everything is stored in a public ledger.
Swing trading
Swing trading is a style of trading that attempts to capture short- to medium-term gains in a financial instrument for a longer period than one trading day. In other words, positions are extended overnight and kept open over a few days to several weeks.
Medium-term trading suits fine rookie traders. Indeed, this stipe does not require so prompt trading decisions as in scalping and does not need as wide trading experience as in long-term trading. A trader does not have to keep close tabs on a market environment, though it is advisable to log in to a trading platform at least once a day.
The practice shows this type of trading is appropriate when trading currency pairs, shares, and futures contracts. On the flip side, swing trading poses bigger risks when trading crypto. Digital money is marked by higher volatility. Besides, price moves of some cryptocurrencies cannot be predicted with accuracy. Therefore, only savvy traders can manage trading crypto.
Advantages of swing trading
- It saves time. A trader does not have to monitor the market around the clock and stare at a trading platform.
- A trader does not have to employ a wide array of technical indicators. It is most appropriate to use trend-following algorithms and level indicators.
- A moderate pace of trading eases anxiety so that a trader is not overwhelmed by emotions which could affect trading.
- Without haste, a trader is able to make well-rounded and sensible decisions.
- A low trading load enables a trader to speculate several instruments at a time.
Disadvantages of swing trading
- A trader has to deposit a significant amount to get started. Following the key rule of money management, a trader should allocate no more than 3% of the deposit to one trade. Therefore, you should have way more money on the deposit than you plan to allocate for trading.
- A trader can manage a relatively small number of positions and gain modest profits.
- A trader runs high risks when extending positions overnight or through a weekend. During a break, the market might be struck by unexpected events which might push market quotes in a direction contrary to the scenario.
Long-term trading
Long-term trading, also known as position trading, refers to a trading style in which a trader will hold on to a position for an extended period of time from a few weeks to a couple of years. Positions traders aim to gain as much profit as possible.
Commonly, traders buy undervalued assets such as newly introduced and little-known altcoins or shares of promising companies. Besides, this trading style is popular on Forex.
To take up this kind of trading, a speculator should meet the following requirements:
- A decent start-up capital is a must-have. Leverage could be a solution, but risks are bound to increase proportionately.
- An important skill is to recognize an undervalued asset. For example, a trader decided to invest in bitcoin because he bet on bitcoin’s growth after it is acknowledged to be a legal payment means. Another market participant prefers to invest in a newly-invented altcoin. He explored its features and predicted that the token would be a roaring success someday in the future.
- A trader should investigate the archives of market quotes and factors which used to influence the asset’s value in the past and are likely to influence in the future.
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Position trading
Let’s look into position trading as a separate method of long-term trading. A market participant aims to exploit a trend at the very most, reaping the highest possible profit. Importantly, a trader neglects the interim ups and downs because he is focused on the overall dynamic which could last for a few weeks and even months. A trader keeps buy/sell positions open for all this time.
Position traders rely on fundamental analysis to predict a long-term outlook, albeit it is complemented by technical analysis. A trader spends little time on trading as such compared to scalping, for example.
A position trader follows these steps:
- Market analysis and opening positions. The key point is to grasp the trend and the preferable point to open a trade which could be found at the beginning and in the middle of the trend.
Oftentimes, a new trend comes into being after a breakout of support/resistance levels. Particular technical patterns may also generate such signals. So, technical analysis will be helpful.
- The market should be monitored from time to time. This is the right time to apply fundamental analysis which enables a trader to grasp catalysts driving the price.
- Closing positions. A trade can be closed either manually or by a stop loss.
The screenshot exemplifies the market entry and exit in position trading based on the use of moving averages. Here we can also watch how a long-term trend resumes after a minor correction.
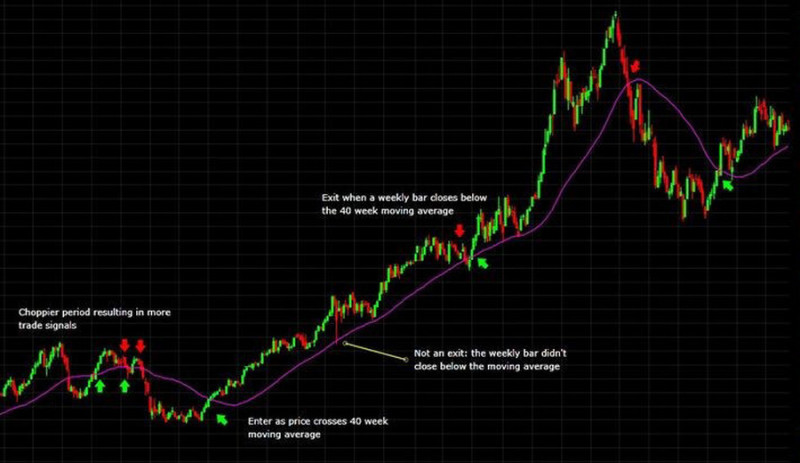
Those who want to take up position trading should realize that it is accompanied by risks. The most serious risk is that a trend might reverse earlier than expected, thus entailing financial losses.
Conclusion
To sum up, all types of trading described above have weak and strong points. There is no all-inclusive method to satisfy the needs of all market participants.
Someone picks scalping as the perfect style of trading. Others prefer long-term trading. As we said earlier, everything depends on the trader’s psychological traits and trading goals.
Rookie traders are advised to practice swing trading because this style suggests the best risk/profit balance and trading itself does not suppose any haste and high load.
After a trader acquires appropriate experience and skills, it makes sense to try short-term or position trading. These two trading styles require profound knowledge and practical skills.









 Back to articles
Back to articles

