
The advent of the internet radically transformed life on Earth. It allowed users from different countries to interact in real time, exchange data, conduct financial transactions, and much more.
However, over time, the internet became centralized and monopolized. As a result, modern developers set out to create a new internet based on blockchain technology. One of the most interesting and innovative projects in this area is Internet Computer, which we will discuss in this article.
To learn more about other unique cryptocurrency platforms, their key features, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as their rankings, refer to the article
"Cryptocurrency rankings."
How modern internet works
When the modern version of the internet first appeared, it offered vast opportunities. People from different parts of the world could communicate, share documents and files, search for information, and complete other tasks. It was an open and decentralized network powered by thousands of independent providers.
Over time, however, the internet became monopolistic and centralized. Today, access to the network is provided by a limited number of large providers like Amazon Web Services or Google, which can impose content access restrictions or change other parameters.
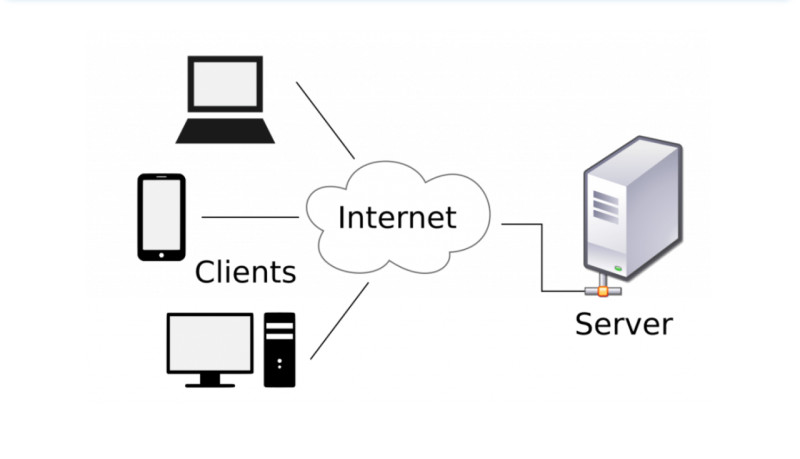
The interaction structure between a person and the web can be described as "client-server," meaning the user receives answers from a server. These servers also store all the information, including personal data that users provide when registering on different websites.
The servers themselves are super-powerful computers owned by private companies, capable of storing vast amounts of data. Currently, large tech companies own these servers and effectively control all user data.
This setup enables government oversight and censorship, negatively affecting privacy. User data can be used for advertising or other purposes.
Additionally, such servers are frequent targets for hackers, aiming to steal personal data. This is particularly concerning when it comes to information that could grant access to bank accounts and other financial details.
All of these factors led developers to the idea of creating a decentralized internet, one that would be truly private and independent. This concept is based on blockchain technology and is known as Internet Computer, which we will discuss in more detail.
Decentralized internet
So, what is a decentralized internet, and who came up with this idea? As mentioned, at a certain point, it became clear that the current version of the internet could not fully ensure user privacy and data protection.
Moreover, users often struggle to find the necessary information because there is simply too much content online. Search engines may display not what users are looking for but what is better promoted on websites, even if it is not relevant to their requests.
Data is stored on the servers of specific companies, and these companies essentially own and manage that data. This means that videos on YouTube belong to YouTube, and tweets on Twitter belong to Twitter, not the authors. These platforms can block or censor content.
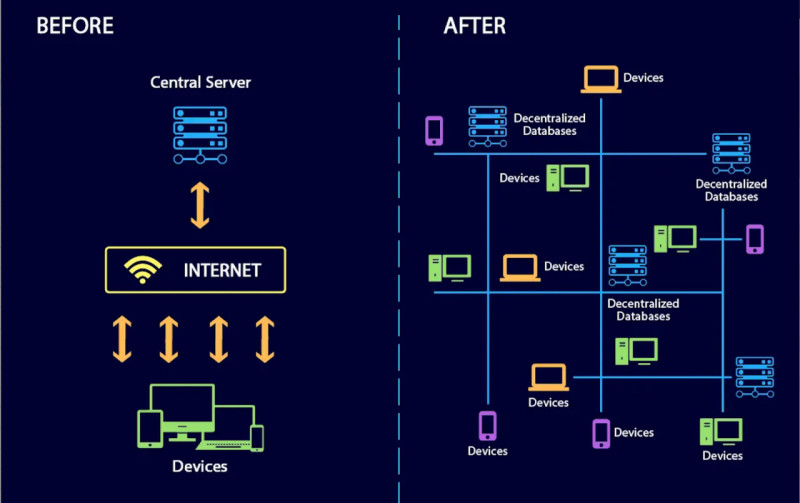
In the concept of a decentralized internet, data is not stored on a single server but is distributed across nodes located anywhere in the world. Moreover, the content creator owns their data, not the platform where it is hosted. Only the author can modify or delete it.
This technology not only ensures protection from censorship but also guarantees the secure storage of any data. Since data recorded in a blockchain cannot be changed or removed, it is impossible to alter even one block without changing all the others. Additionally, because the entire data chain is stored on every participant’s device, it is nearly impossible to change it on all devices.
The decentralized nature and security of blockchain are ensured by these features. Digital currencies are expected to play a central role in this concept, and one such currency has already appeared. It is the ICP cryptocurrency, which we will discuss along with the project it is a part of.
Dfinity Foundation
We have already established that the decentralized internet was proposed as an alternative to the modern internet, aiming to make it open again while enhancing privacy. Based on this concept, a new digital coin, ICP cryptocurrency, was created.
One of the pioneers of this concept is Dominic Williams, who founded Dfinity Foundation in 2016. The name Dfinity comes from two English words, “decentralized” and “infinity,” literally meaning “decentralized infinity.” This formula formed the foundation of the decentralized internet idea.

The company was established in Switzerland but is now international. It employs over 200 people worldwide, including in Switzerland, Germany, the US, the UK, and other countries.
The company’s key goal is to provide the most popular services, such as developing decentralized applications and other services. The project allows users to move away from using centralized and commercial cloud services.
According to the creators of the Internet Computer, the internet should once again become open and accessible. This will be achieved through the Chain Key technology, which is a set of cryptographic protocols made up of various components.
This technology ensures the functioning of the entire system, adding new nodes and forming subnets, which allows for scalability. Additionally, Chain Key is responsible for replacing faulty nodes, restoring subnets, and performing other functions.
Thanks to its strong technological foundation and ambitious ideas, the project attracted attention and funding from well-known investment funds such as Polychain Capital and Andreessen Horowitz, which collectively invested $102 million. Other investors later contributed another $166.9 million to the project.
Technical features of Internet Computer
As mentioned, Internet Computer implements a range of technological innovations aimed at addressing current internet challenges and creating a new service model. The project’s utility currency, ICP cryptocurrency, is used to carry out these tasks.
So, what technological advancements are used in this project, and how do they work? First is the unique Chain Key technology, which allows separate data processing and consensus within the chain. This ensures high throughput and scalability.
The core of Internet Computer's operation lies in special devices known as node machines, connected through a unique protocol and installed in independent data centers. The chain itself consists of several sub-chains interconnected by Chain Key technology.
Smart contracts are supported by the Canister SDK, which simplifies application development by providing developers with essential tools and access to databases.
Canisters are individual computational units that store data about the program's current state, past events, and user actions, remaining isolated from the environment.
Control and management of the chain are handled by a main subnet called the Network Nervous System (NNS), which oversees all processes related to the functioning of the Internet Computer, including adding autonomous data centers and individual nodes.
Additionally, ICP employs a Threshold Relay consensus algorithm, a variant of Proof-of-Stake (PoS). It works by generating a random number by the nodes, which is then used to select the next group of nodes and manage the platform’s protocols.
The chain uses its own programming language, Motoko, enabling developers to build websites and other services. Other languages like Rust and Java are also supported on the platform.
How Internet Computer works
At the core of the chain is the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) blockchain. The structure of the chain is hierarchical, consisting of several layers or blocks.
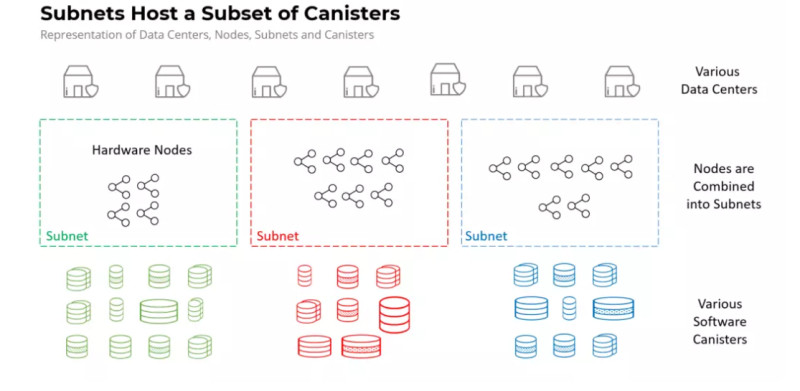
At the lowest level are autonomous data centers, which consist of special hardware nodes or individual computers. Anyone can become a node owner by submitting an application, purchasing the necessary equipment, installing the protocol, and joining the Internet Computer chain.
Multiple nodes can be combined to create a subnet. The more nodes there are, the more subnets can be created, providing greater scalability. Subnets can interact with each other through the Chain Key technology mentioned earlier.
Inside the subnets are software containers, which are computational blocks uploaded by users. These containers are called Canisters, and they consume resources known as cycles.
Cycles act as fuel for computational processes, similar to gas in the Ethereum network. Unlike ICP, whose value fluctuates due to market conditions, cycles have a stable price pegged to the SDR, a currency unit determined by the IMF.
Canisters can work together with other containers, even if they belong to different sub-chains, which improves the scalability of decentralized applications. Additionally, these containers have built-in security against hacking.
The chain’s consensus mechanism requires agreement among nodes at the subnet level rather than across the entire blockchain. This allows operations to run concurrently across multiple sub-chains.
For chain management, the NNS system consists of individual neurons. Each neuron locks a certain number of ICP coins, giving holders the ability to participate in voting and earn rewards for doing so.
ICP cryptocurrency
Now that we have an understanding of the Internet Computer project, it is time to take a closer look at its utility currency, the ICP cryptocurrency. This coin performs several key functions and ensures the operation of the platform:
- Governance: ICP is a governance coin, meaning its holders can participate in voting on the project’s development decisions. This option promotes decentralization and community-driven decision-making.
- Payment of fees: All transaction fees on the platform are paid in ICP tokens, which are then distributed as rewards to validators.
- Staking: Users can stake ICP coins to earn rewards. Staking helps maintain the security and functionality of the platform’s consensus algorithm.
- Participation in system projects: The currency can also be used in applications and services launched on the Internet Computer. Tokens can be converted into neurons and cycles, which are used for computational processes.
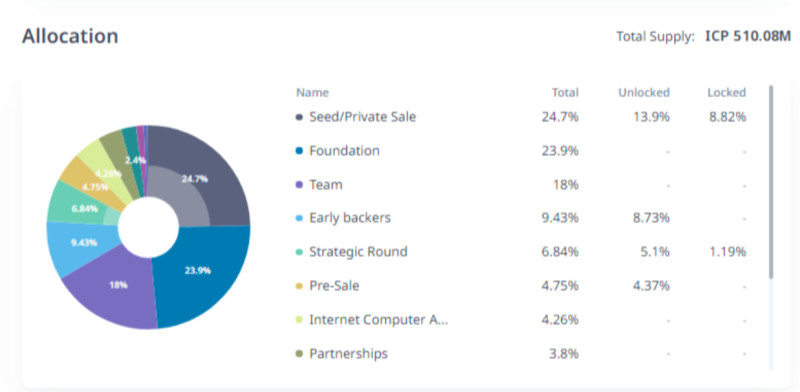
Initially, over 469 million ICP coins were released into circulation, and distributed among developers, investors, and chain participants. Additional tokens were later issued, bringing the total number of ICP coins to over 497 million, with new tokens released weekly.
Since the platform uses a PoS-based consensus algorithm, its native currency cannot be mined. Instead, it can be purchased on cryptocurrency exchanges, received through staking, or earned by providing validator services within the chain.
Currently, the price of one ICP coin is about $17, though its value has seen significant fluctuations. The lowest recorded price was $2.87, and the highest was just over $700.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like other cryptocurrency projects, the Internet Computer platform and its token, ICP, have both positive and negative aspects. Let us take a closer look at its pros and cons.
Key advantages:
- High scalability potential. Thanks to its unique consensus mechanism, this chain has great potential for expansion.
- Support from major investment funds and exchanges. This backing highlights the project’s strong potential and investor confidence, which allowed Internet Computer to secure significant investments early on.
- Decentralization. The platform operates without centralized control. All decisions are made through community voting by ICP holders.
- Community support. ICP token holders actively participate in decision-making, driving their interest in the platform’s development and success.
- Low fees. The chain reduces transaction costs using the unique Chain Key technology.
- Flexibility and interoperability. These features allow the chain to interact with other networks, giving developers broader opportunities.
Main disadvantages:
- Transparency and lack of censorship. While this is a core goal of the project, it also poses risks regarding the type of content that might be available and whether it will be safe for users.
- Regulatory risks. Due to the openness, regulatory bodies might impose restrictions if they see risks, which could affect user interest in the platform.
- High development costs. The platform uses specific programming languages that require specialized skills, limiting the pool of potential developers and users.
ICP future
The development of a decentralized internet is a timely topic, giving Internet Computer and its ICP token strong growth potential if they can overcome the challenges and risks mentioned above. The platform faces stiff competition in scalability and performance, as each new chain aims to outperform others in transaction speed and customer benefits.
However, the Internet Computer is undeniably an ambitious and innovative project. This is evident from numerous partnerships and integrations with other projects, which can give it a competitive edge and provide users with a unique experience.
One notable partnership is with SingularityNET, aimed at integrating artificial intelligence with blockchain technology, which will enhance efficiency and security in the digital space.
The platform’s main promise is an open, censorship-free internet, allowing creators to publish content independently of centralized corporations like Google or Amazon. Additionally, the content's ownership remains fully with the author.
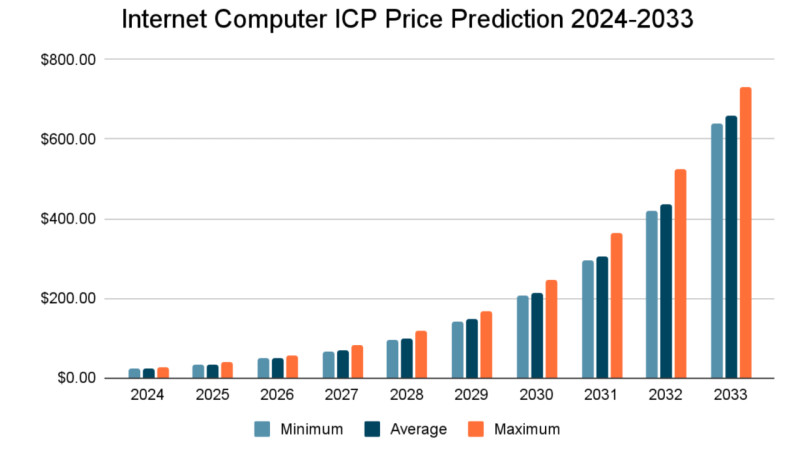
Regarding the ICP token, its price has fluctuated significantly since its launch, showing both rapid growth and sharp declines. The future value of the ICP token will depend on the broader cryptocurrency market and the continued development of the Internet Computer. If the project grows in popularity, demand for its token is likely to increase, leading to a rise in its price.
Conclusion
This article explored the innovative concept of creating a decentralized internet with the Internet Computer platform and its ICP token. The platform aims to revolutionize the current approaches to data transmission and storage.
The goal of the project is to make the internet open and censorship-free, which garners both praise and criticism. The open internet is a plus because content will no longer be blocked by centralized organizations, and ownership will remain with the creators, not the platforms hosting it.
At the same time, there are risks concerning the safety of the content on the network, as well as the possibility of government intervention to block certain harmful materials.
Nonetheless, the concept of a decentralized internet remains attractive. The project team has proposed unique solutions, such as Chain Key technology, which enables the separation of operations and consensus processes.
The network consists of multiple layers, with the lowest being individual nodes grouped into subchains. Subnets process transactions, allowing parallel processing of different operations across various subchains.
User data is stored in containers called "canisters," where smart contracts and other actions take place. These canisters require specific resources known as "cycles" to function.








 Back to articles
Back to articles

