
Thanks to the fact that the first cryptocurrency continues to hold a leading position and remains the most sought-after among all digital currencies, Bitcoin mining ranks first among all other coins. The term “mining” literally translates as “extraction,” since this is the process by which new cryptocurrency units enter circulation.
However, the primary function of mining is to ensure the security of the blockchain and protect it from hacker attacks. Bitcoin mining has its own distinctive features, which we will examine in this article, along with how much one can earn and how to do it legally.
To learn more about the mining process itself, how it has evolved over time, what equipment is currently needed for crypto mining, and how much one must invest before starting to earn, see the article “Mining.”
What is Bitcoin mining?
Unlike traditional money, digital currencies are not put into circulation by any central authority or organization. The process of creating new units of cryptocurrency is similar to extracting precious metals from the earth, which is why it is called mining.
Just as gold miners spend their resources and time to obtain and release gold into circulation, miners use the resources of specialized equipment and electricity to produce new digital coins, including Bitcoin.
The essence of mining is not that digital coins must literally be “found” somewhere. Miners receive new “bitcoins” as a reward for the work they perform — specifically, verifying transactions submitted by users and adding them to blocks.
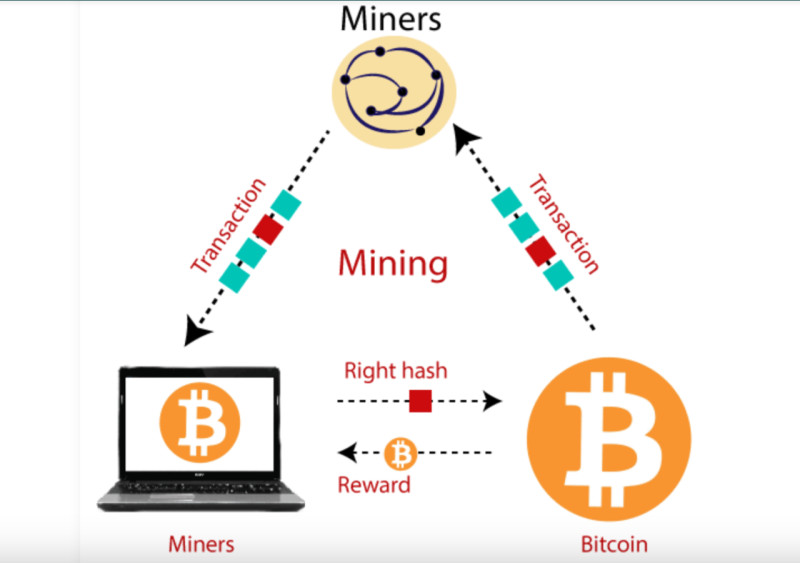
These blocks are then linked together in a single chain known as the blockchain. One of the main features of the blockchain is decentralization — meaning there is no single server where all the data is stored. Instead, the data is stored on many independent devices called nodes.
Thus, the blockchain is a distributed ledger that must be stored in the same state on all devices. This is achieved through a special consensus algorithm called PoW (Proof-of-Work).
This name comes from the fact that participants must prove they have allocated sufficient resources to complete the task. The first to do so receives a reward consisting of two parts:
| Block reward | Transaction fees |
| A fixed amount of newly created coins that subsequently enter circulation. Every four years, the Bitcoin blockchain reduces this reward by half — a process known as halving. At present, the reward is 3.125 BTC. | The amounts users pay for transaction verification. These fees incentivize miners to include transactions in a block, with those offering higher fees being prioritized. The rest remain in the mempool, waiting their turn. |
Why mining is needed
Now that we have a general understanding of what Bitcoin mining is, let’s figure out why it is needed at all and what functions it performs. After all, generating new coins and putting them into circulation is not the only — nor the main — goal of mining.
The main function of mining is to achieve consensus within the chain and protect it from hacker attacks. As we have seen, the blockchain is essentially a ledger whose copies are stored on a large number of independent devices, containing records of all Bitcoin transactions for the entire history of its existence.
This ledger records all operations carried out on the Bitcoin chain. Transactions are grouped into blocks, with each new block being created approximately every 10 minutes. In addition to transactions, each subsequent block contains a reference to the previous one, ensuring the chain’s continuity and preventing any alterations to past records.
Thanks to decentralization, there is no central authority that assigns transactions to nodes for processing. Instead, consensus and coordination among miners are achieved collectively according to the Bitcoin chain protocol.
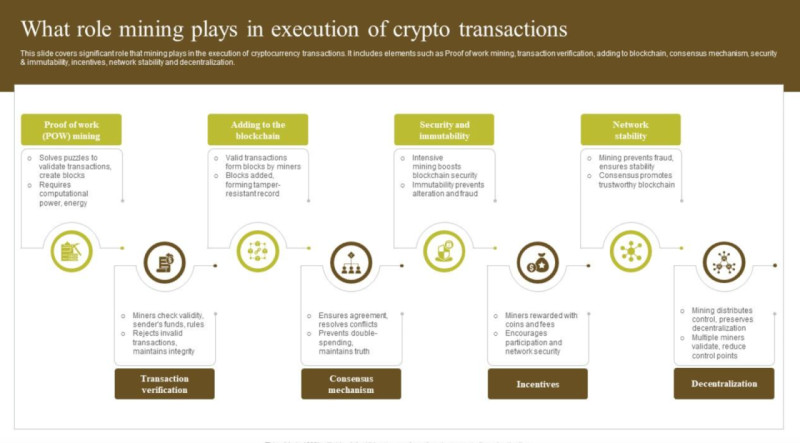
Most nodes store the ledger’s history, verify the validity of transactions, and pass new blocks on to other nodes for review. Once one of the chain participants successfully mines a new block, they broadcast it to all other nodes for verification. After verification, the block is added to the network, and all nodes receive an updated copy of the ledger.
However, in every chain, there is also a smaller group of participants who compete to solve the blockchain’s computational tasks as quickly as possible — thereby winning the right to add the next block. The one who finds the solution first is rewarded with new bitcoins.
Before a block is added to the chain, it must be verified by all nodes, which significantly complicates any attempt at a hacker attack. To validate a fraudulent version of the ledger, an attacker would need to control more than 51% of all nodes — a practically impossible task.
How Bitcoin mining works
Let’s break down the process step-by-step. The full algorithm is described in detail in the foundational document — the white paper — published when any new cryptocurrency is launched.
The process begins when a new transaction is made on the network, visible to all participants. Each node starts collecting new transactions into a block while simultaneously working to solve a complex mathematical problem and providing proof of work.
When one participant finds the proof, they send the block to all other nodes for verification. The block will only be accepted if all transactions in it are valid and the coins involved have not been double-spent (i.e., no same coins are sent to multiple recipients).
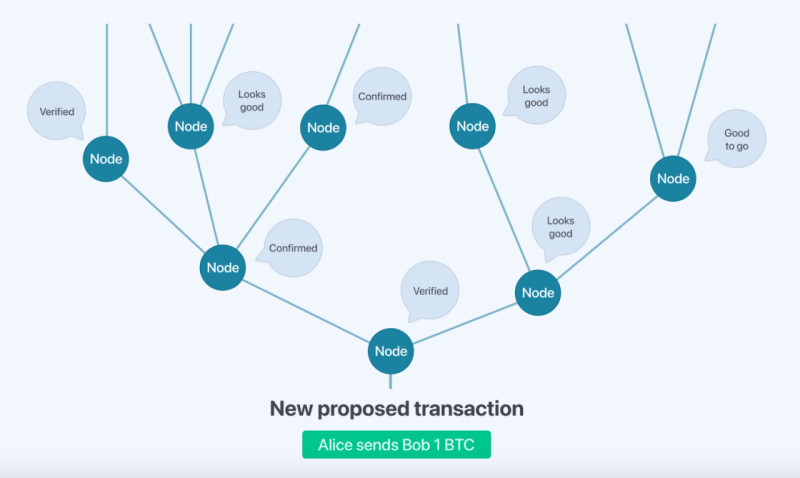
Nodes signal their agreement by starting work on the next block in the chain, using the hash of the accepted block as the “previous hash.” Hashing is the process of converting data into a special code, and a hash is the unique string of characters representing that data.
Miners are free to choose any transactions from the mempool for inclusion in a block. Typically, they prioritize transactions with higher fees. The first node to finish verifying the transactions submits them to other participants for confirmation.
Nodes verify the block’s validity by checking two main conditions:
- All transactions in the block are valid (no double-spending).
- The new block references the previous block and is numbered as the next in the chain.
Once verified, the block is propagated throughout the network, and an updated copy of the ledger is formed.
Sometimes, more than one participant manages to create a new block almost simultaneously. Because nodes are distributed across different geographic regions and time zones, small delays may occur.
In such cases, the newly created blocks will differ, as each node selects its own set of transactions. When two miners add different blocks to the chain at the same time, two versions of “truth” temporarily exist. However, the network eventually favors the chain that grows faster and recognizes it as the valid one.
Changes in mining difficulty
Given how the process of generating new blocks works, it may seem from the outside that Bitcoin mining is a very simple activity available to anyone. It might appear as though money is made “out of thin air,” since a person doesn’t need to make any effort—machines do all the complex calculations.
However, it’s not that simple. In fact, the mining process is constantly becoming more challenging. This mechanism is embedded in Bitcoin’s code itself: as the number of participants in the network increases, mining gradually becomes more difficult. This is done to maintain a steady rate of adding new blocks—about 10 minutes per block.
The difficulty level is adjusted every 2,016 blocks, which takes roughly two weeks. The total computing power of the network also plays a role: when it increases, the difficulty rises, making mining harder for everyone; when it decreases, the difficulty drops as well.
This helps ensure a more even flow of new coins into circulation, as their total supply is capped at 21 million. Therefore, mining Bitcoins indefinitely is impossible. No matter how much computing power is devoted to mining, the total number of coins created will remain unchanged.

When Bitcoin first appeared, it was possible to mine it on a regular desktop computer or laptop. At the time, nobody saw any real value in it—users mined Bitcoins simply for fun, sent them to one another, or spent dozens of coins on small purchases.
However, within just a year, the situation changed drastically: the first cryptocurrency exchanges appeared, allowing people to trade digital coins for real money. This drew many more users to mining, and with it came the automatic increase in difficulty coded into the currency.
The computing power of regular processors soon became insufficient, so users began using graphics cards. Often, 6–8 GPUs were installed on a single motherboard, greatly increasing mining power and speed. This marked the beginning of the first mining farms.
As the process kept getting harder, miners needed even more powerful devices. Graphics cards were eventually replaced by specialized hardware—ASIC miners—designed specifically for solving blockchain puzzles. Today, the largest mining farms consist almost entirely of such devices.
How much can you earn?
Even though mining is constantly becoming more difficult and the block reward is decreasing, Bitcoin mining remains attractive to many users. This is likely because it still tends to be more profitable than mining most other cryptocurrencies.
However, to understand how much one can actually earn, it’s important to know what expenses are involved. The two main cost categories are:
- Equipment: purchasing specialized mining hardware, setting it up in a suitable facility, and covering repair and maintenance.
- Electricity: mining consumes enormous amounts of energy, so having access to cheap electricity is a major advantage.
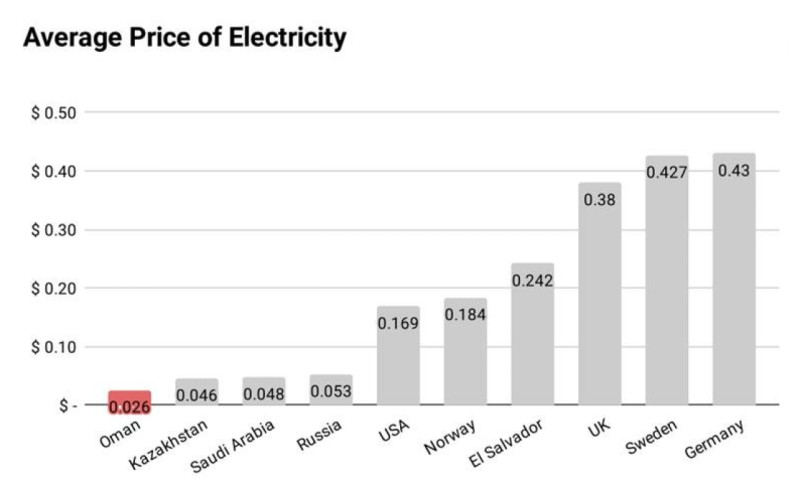
Equipment can be purchased second-hand, but it will be less efficient than new machines and will require more maintenance. Therefore, the only reliable way to reduce costs is to lower electricity expenses, for example, by using alternative energy sources.
If we make a rough estimate of the cost of setting up a small home mining farm, even the most modest setup will cost at least $2,500. The payback period for such a farm is typically no less than 1.5–2 years.
Importantly, every four years, the Bitcoin network undergoes a “halving” that cuts the block reward in half. In 2009, the reward for mining one block was 50 BTC; today, it has dropped more than 15-fold to just 3.125 BTC.
Depending on electricity prices in different regions, the estimated cost of mining one Bitcoin ranges from $15,000–$20,000 to as high as $45,000. Profit margins from mining a single coin can be anywhere from 20% to 50%, depending on the exchange rate and other factors.
Environmental impact
In light of growing global concerns over worsening environmental conditions, Bitcoin mining has drawn extremely negative reactions from many people. This is primarily due to its massive electricity consumption and CO₂ emissions.
The Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm used in Bitcoin’s blockchain indeed requires a substantial amount of energy. With each passing year, the mining process becomes more complex, demanding more powerful equipment, larger-scale operations, and, consequently, higher electricity consumption.
Governments in many countries have been so concerned about this that they have banned Bitcoin mining altogether. One of the most striking examples is China, which was once a global leader in this field (accounting for more than 45% of all mining activity). However, in 2021, China imposed a complete ban on mining, forcing all miners and their farms to leave the country.
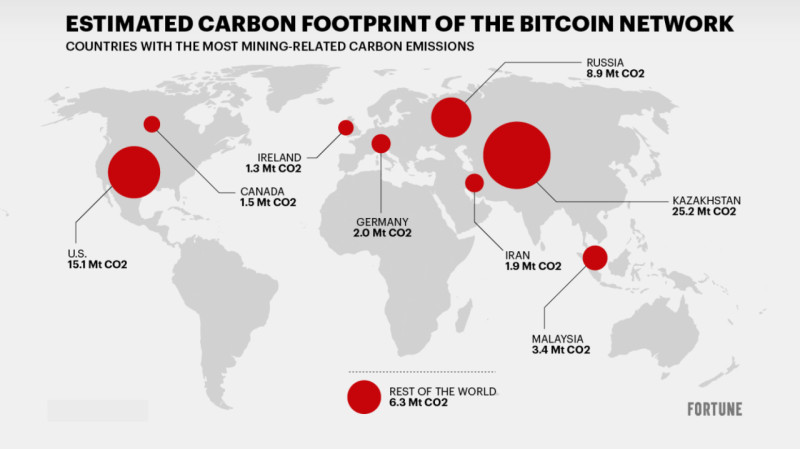
High energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, which in turn lead to climate change. It is estimated that Bitcoin mining consumes about 91 TWh of electricity annually (more than Finland’s yearly energy consumption), with a carbon footprint of around 65 million tons of CO₂ per year (approximately 0.2% of global emissions).
Supporters of cryptocurrencies are attempting to address the problem of excessive energy use by turning to “green” energy — renewable sources such as wind, solar, and hydro power. Currently, over 50% of electricity for mining comes from renewable sources.
However, high energy consumption and carbon emissions are far from the only problems caused by mining. When Bitcoin mining equipment becomes obsolete, it generates significant amounts of electronic waste. In addition, high energy usage can overload power grids and even cause outages.
In response to these environmental challenges, many developers of new cryptocurrencies have adopted alternative consensus mechanisms. One of the most popular is Proof-of-Stake (PoS). In such blockchains, the role of miners is performed by validators.
Validators verify transactions and add them to blocks. Becoming a validator does not require purchasing any special equipment; one simply needs to acquire a certain amount of the cryptocurrency in question and lock it in an account, meaning it cannot be traded or spent.
Legal aspects
Various operations with digital currencies, including Bitcoin mining, are legal in most countries worldwide. However, certain nuances should be considered before engaging in this activity. This section examines those aspects in more detail.
First, it should be emphasized that mining is legal in many countries. However, as mentioned earlier, there are states where cryptocurrency mining is prohibited, largely due to concerns over its negative environmental impact (for example, China).
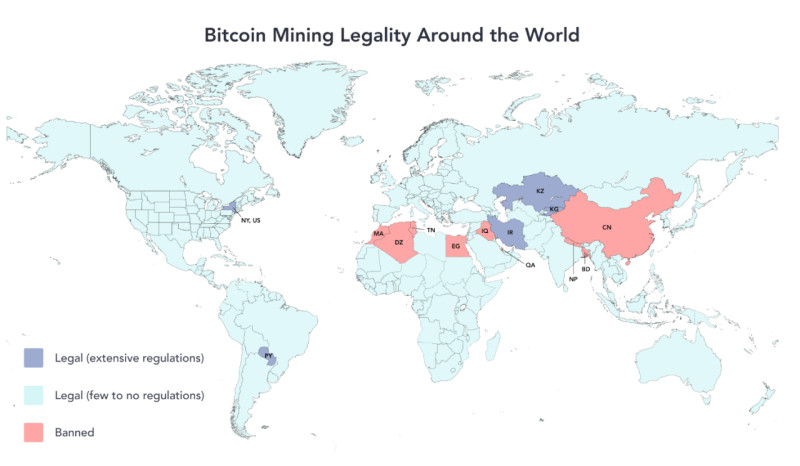
Nevertheless, in some countries where mining is allowed, users are prohibited from using subsidized electricity rates and must instead pay commercial tariffs. Many attempt to circumvent this rule, but if a power company discovers such a violation, it has the right to recalculate charges at the highest applicable rate.
Moreover, operating a mining farm at home can cause disturbances to neighbors — such as excessive noise or power grid overloads — which in some cases may result in accidents. In such situations, the miner may face administrative or even criminal liability.
In most countries, cryptocurrency mining is classified as an entrepreneurial activity, and one of the most important aspects of any business is taxation. Typically, miners are subject to income tax, with rates varying by country from 12% to 20%, although in some jurisdictions they can reach 45%–55%.
The list of countries where mining is legal and highly popular is topped by the United States and Russia, with China also in the top three until 2021. Among European countries, Iceland is a leading supporter of mining thanks to its low-cost electricity derived from renewable sources.
In Latin America and Africa, mining is gaining popularity and is even becoming a primary source of income for some people amid economic crises. However, in most of these countries, there is no clear legal framework regulating cryptocurrency mining, which can create legal risks for miners.
Tips for beginner miners
We have already discussed various aspects of cryptocurrency mining in detail. Many readers of this article may become interested and want to start mining Bitcoin. In this section, we have compiled key recommendations for beginners.
- Choosing a cryptocurrency. Commonly, the starting point is selecting which cryptocurrency to mine. In this case, the choice is obvious: Bitcoin, the first and most attractive of all digital currencies. Its popularity is driven by the potentially high profits from mining new coins.
- Purchasing equipment. It is important to understand that competition in this field is extremely high, so you will need the most powerful and up-to-date devices, assembled into a mining farm. This also involves buying and installing power supply and cooling systems, along with other components.
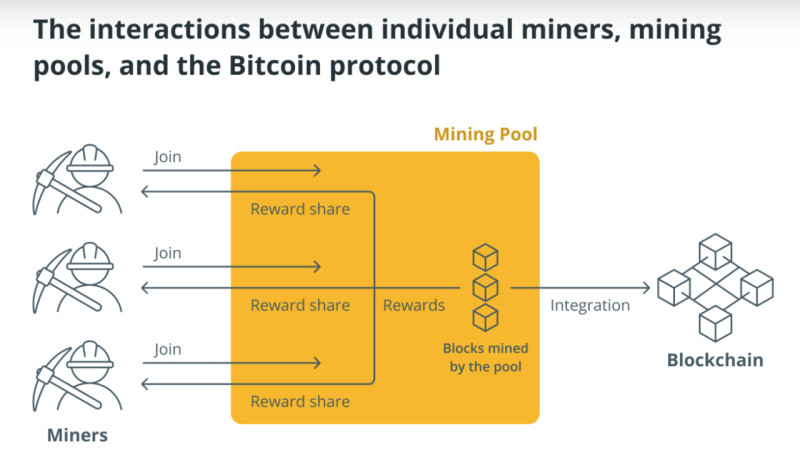
- Instead of setting up your own farm, you can join a mining pool, meaning you combine efforts with other miners to mine cryptocurrency together. The main advantage of a pool is the distribution of tasks among participants; the main disadvantage is that the reward must also be shared.
- You will need a wallet to store the mined coins. If you do not plan to use the cryptocurrency regularly, it is better to store it in “cold wallets” that are not connected to the internet, making them harder to hack. If you intend to use the coins frequently, a “hot wallet” is more convenient.
- Assess your earning potential realistically, taking into account all related expenses. Mining is not “money from thin air” — it requires substantial initial investment, and whether it pays off depends on many factors.
- If you have the opportunity to place equipment in regions with low electricity costs, take advantage of it. However, do not break the law by, for example, setting up a mining farm in your grandmother’s apartment to benefit from reduced rates — in the end, such “savings” can lead to heavy fines and recalculations at the maximum tariff.
- To legalize your mining activity, you must pay taxes. In most cases, income tax applies. In some countries, miners are also required to register as individual entrepreneurs.
Conclusion
In this article, we have examined what Bitcoin mining is, why it exists, and how it works. The process of creating digital coins consists of several stages: miners verify transactions initiated by network users, then add them to blocks, which are linked together into a continuous chain.
In Bitcoin’s blockchain, creating a new block takes around 10 minutes. To maintain a consistent mining speed, the difficulty adjusts automatically: when more participants join the network, mining becomes more difficult; when fewer nodes are active, it becomes easier.
In the early days, Bitcoin could be mined on a regular laptop or PC, but now it requires specialized, powerful, and expensive equipment. Moreover, mining is highly energy-intensive, which raises concerns about its environmental impact.
To reduce environmental harm, some miners are turning to renewable energy sources. In addition, the legal aspects of mining should not be overlooked: in most countries, mining is classified as an entrepreneurial activity and is subject to taxation.








 Back to articles
Back to articles



