This article is for those who wish to learn the art of Bitcoin shorting from scratch – one of the most dynamic and potentially profitable strategies in the cryptocurrency market.
Initially, we will attempt to explain the meaning and internal logic of this trading strategy, aiming to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of how to short Bitcoin. By the end of the reading, readers should have a foundation for further, deeper exploration of the topic.
We will start by examining the unique characteristics of the cryptocurrency market, which will provide a solid base for understanding the sections that follow. We will discuss which exchanges and tools are best suited for effective shorting. Then, we will explain the basic principles of applying fundamental and technical analysis, as well as the purposes of the short-selling strategy. Finally, we will address risk minimization and key capital management rules.

What attracts traders to Bitcoin?
Cryptocurrencies were created to offer an alternative to traditional banking and government systems. Bitcoin became the first instrument of decentralized financial operations, introducing a new approach to storing and transferring value.
Bitcoin emerged in 2009, with interest in it and other cryptocurrencies beginning to grow in the 2010s, driven by several key factors. The most significant of these was Bitcoin's impressive price increase, which drew the attention not just of investors and crypto enthusiasts but also of the wider public.
This led to a surge in new cryptocurrency projects and companies, creating a "crypto craze." However, the subsequent "crypto winter" – a period of decline and stabilization – highlighted the sector's volatility and unpredictability, as well as its dependence on global economic processes. Now, the crypto industry is entering a more mature and stable development phase, but volatility remains its distinguishing feature.
Bitcoin spawned a whole new class of assets based on a full or partial rejection of traditional money. Crypto optimists believe this marks the beginning of a radical transformation of the entire financial system. Blockchain technology, which can make transactions more secure, simple, and accessible, especially compared to international interbank transfers, supports this view. At the same time, crypto skeptics view Bitcoin as a speculative bubble that will eventually burst and suggest that major central banks will never legalize private cryptocurrencies, especially due to their use in the "gray" and "black" sectors of the economy.
Bitcoin's maximum value relative to the dollar was recorded in November 2021, exceeding $67,500. The record increase in value was driven by a variety of factors, including increased interest from institutional investors, partial recognition of Bitcoin as a store of value, and heightened overall attention to cryptocurrencies amid government stimulus measures during the coronavirus pandemic.
Traders are primarily attracted to Bitcoin due to its volatility and high investment potential for both short-term and long-term trading. Derivatives based on it, such as futures, have become an important part of trading portfolios as an additional way to gain profits. Despite the high risks, private and institutional investors turn to them for speculation and hedging. A proper understanding of the specifics of trading these assets opens access to a new, high-income, and dynamic market.
Peculiarities of cryptocurrency market
Bitcoin Capitalization in Comparative Analysis.
To understand the scale of the cryptocurrency market, it is useful to compare it with traditional financial markets. As of mid-December 2023, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies reached an impressive $1.61 trillion. This is comparable to the valuation of the world's largest corporations, such as Alphabet Inc., which has a capitalization of $1.66 trillion. Bitcoin, at the time of writing, accounts for about half of the entire cryptocurrency market with a capitalization of approximately $834.27 billion, comparable to companies like Tesla and Berkshire Hathaway.
On one hand, this demonstrates Bitcoin's growing influence in the global economy. The capitalization of traditional companies is supported by the value of assets, revenue, and growth prospects, providing a more predictable and stable valuation. On the other hand, the capitalization of cryptocurrencies is based solely on market demand and supply. Thus, the comparable capitalization figures of traditional companies and cryptocurrencies have different natures and degrees of reliability.
Mechanisms of Bitcoin Price Formation
The price of Bitcoin is formed based on market demand and supply and is not backed by physical assets or government guarantees, unlike traditional currencies. While the exchange rate of, for example, the EUR/USD pair depends on economic indicators, political events, and the monetary policy of central banks, the value of Bitcoin depends on the overall investment climate, news in the cryptocurrency sphere, and technological changes in the industry.
Understanding these characteristics helps traders better comprehend how the cryptocurrency market functions compared to traditional markets. The cryptocurrency market is striving to become a significant part of the global economic system, offering unique opportunities for trading and investment, though they are accompanied by high risks and uncertainty.
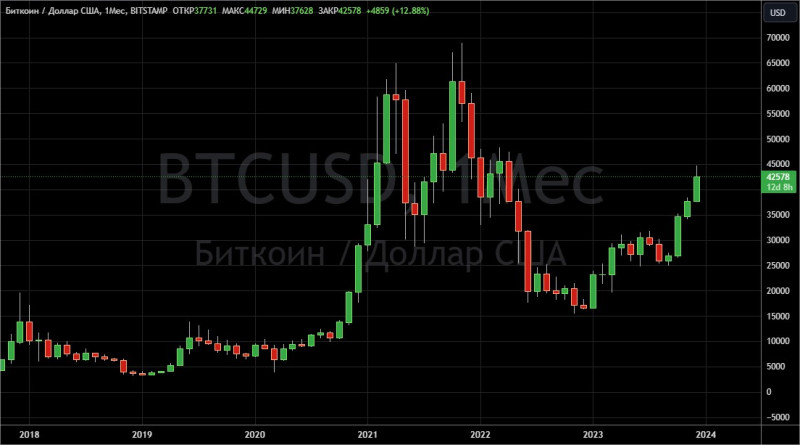
Bitcoin’s volatility
Volatility is a measure of the variability of an asset's price over a specific period. The high volatility of Bitcoin means that its price is subject to rapid and significant fluctuations.
Let’s have a look at the recent data. Over the last month, the value of Bitcoin has increased by approximately 20%, and over the last six months, by 60%. In comparison, shares of Alphabet Inc. (Google) have lost about 2% of their value in the last month and have increased by just over 5% in the last six months. However, there are no guarantees that over the next six months, the price of Bitcoin will not fall even lower than it was six months ago.
Illustration of volatility in numbers.
Imagine that six months ago, you invested $1,000 in Bitcoin and Google shares. Given the aforementioned price changes, your investment in Bitcoin would have increased to $1,600, while your investment in Google shares would have only grown to approximately $1,050. However, it's important to remember that the same degree of volatility can also lead to significant losses in the short term.
The high volatility of Bitcoin can be seen as both positive and negative, depending on your trading strategy and risk appetite.
- Pros: For active traders, increased volatility presents many opportunities for speculation and quick profit-taking. This is especially relevant for short-selling strategies.
- Cons: High volatility increases the risk of losses, especially for those who prefer long-term investments or are less experienced in trading. Fast and unpredictable price changes can lead to significant losses over short periods.
Bitcoin's volatility is a double-edged sword in the cryptocurrency market. It represents both great opportunities and significant risks. Understanding and being able to work with this volatility is a key skill for a crypto trader.
Where to trade cryptocurrencies?
Types of Exchanges and Brokers
Crypto traders have the choice between specialized crypto exchanges and traditional forex brokers.
Cryptocurrency exchanges can be decentralized or centralized. Decentralized exchanges offer greater anonymity and lack regulatory oversight, although they can be more challenging for beginners to use. On these platforms, cryptocurrency trading occurs directly between users with automatic commission charges.
Centralized crypto exchanges, such as Binance, usually strive to meet regulatory requirements and require identity verification. These platforms can freeze accounts and suspend trading at the authorities' request or at their own discretion. However, they offer a broader range of trading instruments compared to decentralized crypto exchanges.
Forex brokers and dealing centers have also started offering cryptocurrency trading services. This is particularly convenient for short-selling strategies, as they mainly work with derivative instruments, such as cryptocurrency futures. Unlike crypto exchanges, they often limit trading to only the largest coins, but allow simultaneous trading in currency pairs, as well as futures on stocks, indices, metals, and commodities. This facilitates portfolio diversification and continues trading during periods of "crypto winter" and reduced activity.
On exchanges, traders can use the following derivative instruments suitable for short trading:
- Cryptocurrency futures.
- Contracts for Difference (CFDs).
These instruments allow traders to get profits from predicting Bitcoin's price without the need to directly own the cryptocurrency, using traditional trading platforms like Metatrader.
Margin Requirements and Leverage
When choosing a trading platform, it's important to consider the terms of margin requirements and leverage. Margin is the amount needed in your account to maintain open positions. Leverage allows for increasing the volume of trades using borrowed funds but also increases the risk of losses.
The choice of platform for trading cryptocurrencies depends on your goals. For long-term investments (long positions), spot trading is best suited. On decentralized crypto exchanges, this can be done anonymously, as if you were buying a gold coin from a stranger and storing it at home. However, for short selling, Bitcoin derivatives are more convenient and effective. It's important to carefully study the terms the exchange or broker provides.
How to short Bitcoin
Short selling, or shorting, represents a market transaction that allows traders to profit from the decline in the price of assets. The trading strategy for short selling is to make a profit based on the accurate assumption that the price of the selected asset will decrease.
An example of the most famous short selling in history is the event described in the movie "The Big Short," where hedge fund manager Michael Burry – brilliantly played by Christian Bale – personally made $100 million, and the profit for his fund's investors exceeded $700 million. For those interested in the topic, this film is a must-watch.
Let's consider a fictional, yet possible example of short-selling Bitcoin:
Suppose a trader thinks that there will be a sharp crash in the crypto market. For instance, it becomes known that a company will soon announce the development of a quantum personal computer, which, according to experts, could potentially crack blockchain. Such news could trigger panic in the market if it gets picked up by the media. What to do in such a situation?
- You open a short position on Bitcoin for $1,000 at the current rate, say, $50,000 per BTC.
- The assumptions are justified, and a week later, the price of Bitcoin falls by half – to $25,000.
- You close the position, locking in a hypothetical profit of about $500 (based on the difference in the opening and closing price of the position).
A week later, it turns out that the news was fake, and the blockchain remains secure. The market begins to recover, but you have already made approximately $500.
Why "approximately"? When opening a position, it is important to account for margin interest and broker commission. These costs will be automatically accounted for by the broker and can reduce your final profit. The commission for opening a transaction is usually small, but the interest on the margin could significantly impact the final outcome. It's important to remember: the longer a short position lasts, the less chance of making a profit and the higher the risk of losses. This is why such a trade is called "short" – it implies quick execution.
How to calculate profits from trade?
The formula for calculating profit from short sales, taking into account margin, commission, and leverage, can be represented as follows:
Profit = (Selling Price − Purchase Price) × Position Size × Leverage − Margin Interest − Commission.
Where:
Selling Price is the value of the asset at the time of the transaction opening.
Purchase Price is at the time of the transaction closing.
Position Size is the amount of the asset being sold.
Leverage is the ratio of funds provided by the broker to your own funds. For example, if you have $1,000 and the leverage is 1:10, you can open positions up to $10,000.
Margin Interest is the interest charged by the broker for using borrowed funds. This amount depends on the size of the borrowed funds and the interest rate.
The commission is the fee paid to the broker for opening the transaction.
How much will remain of the $500 profit from our example? It is strongly recommended to perform this calculation yourself, at least twice: first, when choosing a broker and studying their terms, and second, when assessing the risks and potential profit of the chosen trading strategy.
How to determine the appropriate time for shorting?
Short sales are a key strategic tool used by traders for various purposes:
- Hedging long positions – this protects long positions from risks associated with unforeseen market situation changes. Short trades help regulate the balance in the portfolio, reducing overall risk and increasing the potential for long-term profitability, regardless of current volatility or short-term market trends.
- Use in complex automated trading systems – these systems create a multitude of opposite positions, thereby minimizing risks for the investor.
- Opening short-term sell trades in response to market conditions – often, this is a reaction to certain market changes, based on technical analysis of price charts or news background. For example, it could be a response to unusual asset price behavior caused by dubious informational cues.
An excellent example of effective short selling is the rise and subsequent fall in the value of Dogecoin, triggered by a series of tweets from Elon Musk. While many rushed to buy Dogecoin, experienced traders understood that the perfect moment for shorting would soon arrive. They realized that the unjustified and artificially created demand would ultimately lead to a price drop, providing an opportunity to profit from short positions.
Determining the appropriate time to open a short trade requires a deep understanding of the market, trend analysis, and news background. Effective strategies are the result of well-considered decisions based on strategic planning and risk management. Mastering these skills means mastering the profession of a trader.
Fundamental analysis of BTC
Fundamental analysis in traditional finance is a method of evaluating the real value of an asset compared to its current market price. Warren Buffett, the famous investor and founder of one of the world's largest companies, Berkshire Hathaway, is known for using this approach, earning him the nickname "The Oracle of Omaha." His investments, made after a long and careful study of financial reports, seemed almost "prophetic" to the average person. However, since cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, lack financial reports for analysis, it might seem as though fundamental analysis is not applicable to them. But this is not entirely true.
BTC correlation with other indicators.
Lately, traders have noticed a stable correlation between the price of Bitcoin and other economic indicators, such as the S&P 500 index of the largest American companies and, especially, the Nasdaq technology index. This allows the use of classic fundamental analysis tools to predict BTC/USD price movements, focusing on key events in the economic calendar.
Therefore, crypto traders also closely monitor changes in the US Federal Funds Rate. Changes in interest rates affect risk appetite: lower rates decrease borrowing costs and stimulate investments, which can affect the BTC price. An important indicator is also, for example, the US Consumer Price Index, which is a key indicator of inflation. Rising prices may prompt the central bank to raise interest rates, which, in turn, affects the investment climate, etc.
Since cryptocurrencies today are an integral part of economic life and their owners are located in every corner of the world, the basic principle of Bitcoin's fundamental analysis involves careful study and analysis of global economic trends.
Technical analysis of BTC
Technical analysis of Bitcoin involves studying historical market price and trading volume data. The core principle of this approach is that historical patterns and trends often repeat themselves, reflecting the behavior of market participants.
Let's consider a simple example of technical analysis. Suppose you're analyzing a Bitcoin chart and notice a Head and Shoulders pattern. According to widely accepted theory, this pattern often precedes a change in trend from upward to downward. Using this information, along with indicators or news, a trader might open a short position.
Why does this approach work? Researchers find an explanation in psychology. People tend to act similarly in similar situations, which is reflected in the price dynamics on the charts. Thus, technical analysis combines the use of mathematical models with an understanding of human behavior, allowing for a relatively high probability of identifying potential entry and exit points in a transaction.
Important elements of technical analysis include support and resistance levels – lines on the chart indicating areas where the price of an asset often stopped or changed direction, as well as chart patterns like triangles, flags, and Head and Shoulders, which can indicate the future direction of price movement.
Among the most common mathematical tools of technical analysis are:
- SMA (Simple Moving Averages) helps identify the general direction of the trend by graphically displaying the average value over a certain time interval.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is used to determine the strength and direction of the trend, as well as possible points of its reversal.
- Bollinger Bands help identify overbought or oversold conditions of an asset, as well as market volatility.
*The mentioned method is basic but not the only one.
Proper use of technical analysis tools can provide significant advantages in predicting price movements. However, like any other analysis method, it does not guarantee 100% success in every transaction and should be used in strict accordance with the rules of the trading strategy and risk management tools.
Risks and capital management
Understanding the risks is critical in trading. Before opening a position, it's extremely important to assess the risks, especially when leverage is used, which can lead to significant financial losses.
- Losing the entire deposit is one of the main risks of margin trading (and a trader's nightmare). A sharp increase in an asset's value can quickly deplete the margin and may lead to a total loss of invested funds. Traders must be able to stop in time and liquidate positions to avoid irreversible consequences.
- Costs of margin maintenance. Holding a short position for an extended period can result in interest on borrowed funds reducing the profitability of the trade so much that it wipes out all profit.
- A short squeeze is a situation where a sharp increase in an asset's value forces traders with short positions to close them, further amplifying the rise in quotes and bankrupting those who trade short. Traditional exchanges suspend trading of an instrument in the event of a short squeeze; crypto traders need to consider these risks on their own.
The main tool to combat these risks is the use of stop-loss orders to limit losses and strict adherence to risk management rules. The size of potential losses from each trade should be clearly defined and match the limits set by your trading strategy. This helps avoid catastrophic losses and maintain portfolio resilience, even in volatile market conditions.
Capital management and loss limitation are key aspects of an effective trading strategy. It is crucial for a trader to recognize and correct their mistakes in time, which helps minimize potential losses and preserve capital for long-term trading.
Conclusion
In this article, we have briefly but comprehensively discussed the specifics of trading short in Bitcoin. For a more detailed exploration of the topic, we recommend studying the following materials:







 Back to articles
Back to articles

